WHERE GLOBAL BIOTECH LEADERS CONNECT
We connect leaders of innovative biotech companies with key stakeholders, investors, and advisors for meaningful relationships, potential investment opportunities, strategic collaborations, and a deeper understanding of the biotech landscape.
For more than 20 years, our targeted, exclusive events have addressed the opportunities and challenges in today’s biotech industry.
Upcoming Events
Join the best in biotech and discover the next level of must-attend investor, business development, and C-level events.
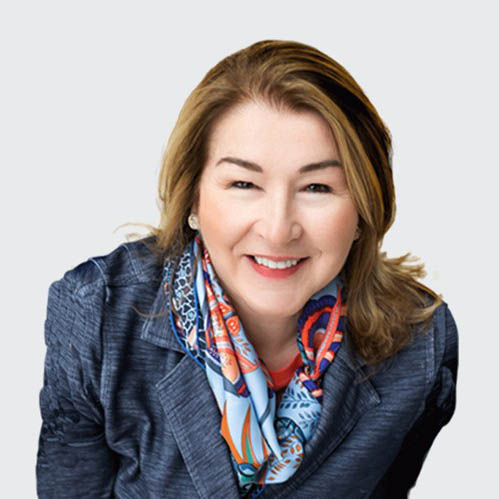
Who We Are
Demy-Colton is a respected leader in biotech investor conferences and highly targeted leadership events. Get to know us.
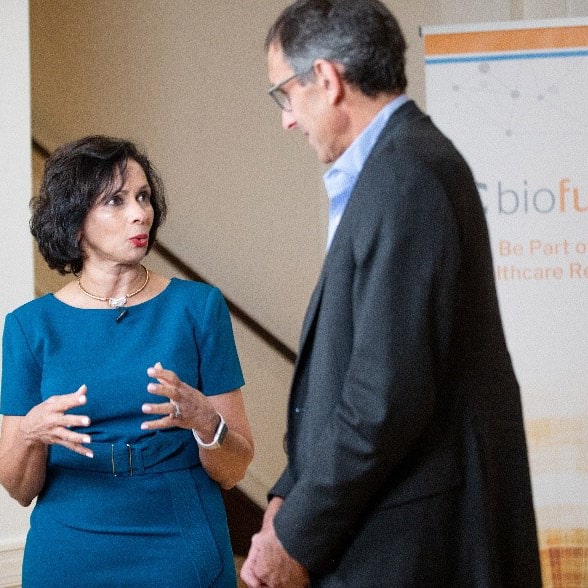


What We Do
See how we create communities that foster lasting and mutually beneficial relationships.

Virtual Salon Series
The Demy-Colton Virtual Salon Series delivers cutting-edge insights from key opinion leaders in the life science and digital health industry. Industry leaders and distinguished guests gather for monthly complimentary discussions to explore the most important topics in healthcare.
United by Individuality, Defined by Inclusivity
Demy-Colton is committed to inclusion across race, ethnicity, gender, age, religion, identity, and experience—it is who we are. We know that diversity drives today’s best companies forward. It is the foundation for our team, who we consider family. We thrive when everyone can bring their full, authentic selves to work. Today and every day, Demy-Colton is committed to bending the arc toward a more just and inclusive society that benefits everyone. We continue to build a culture that encourages, connects, and celebrates diverse voices in healthcare.






